

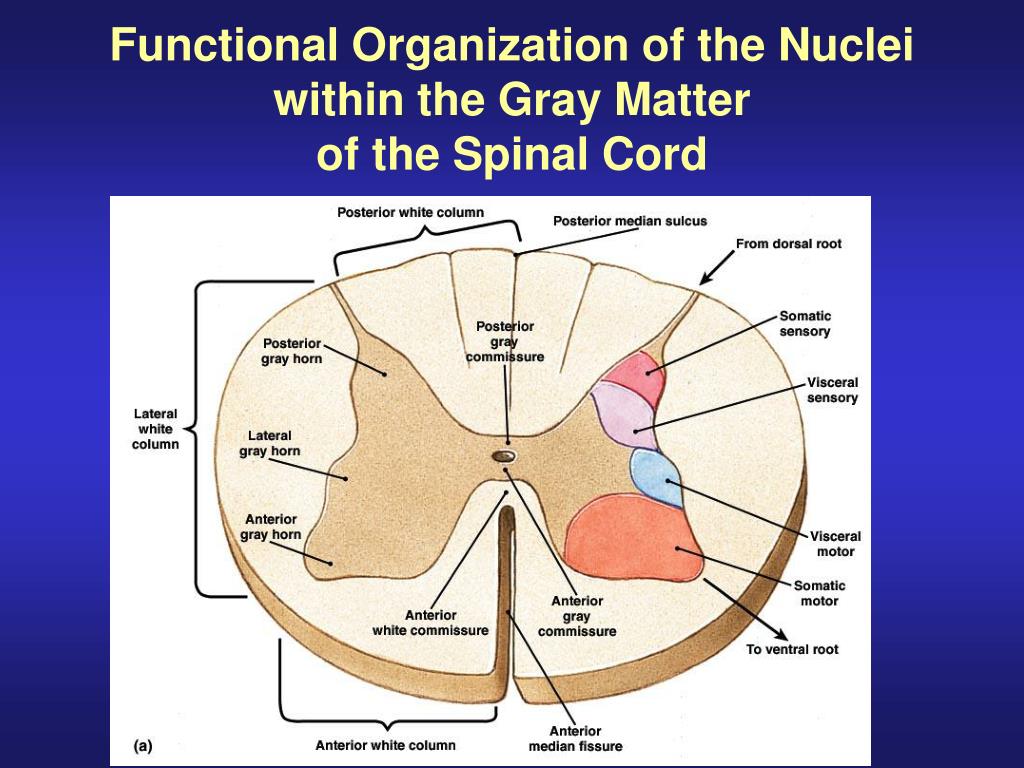


In general, fibers found posteriorly process and relay sensory information, fibers found laterally are preganglionic visceral motor neurons and somatic motor fibers are found anteriorly 4. Lateral columns primarily contain the corticospinal tracts which are the principal motor pathway connecting the cerebral cortex to spinal motor neuronsĪnterior spinal commissure is located between the posterior-most extent of the anterior median fissure anteriorly and the ventral grey matter commissure posteriorly 5. The white matter contains nerve fibers or tracts and is divided into anterior, dorsal and lateral columns (also known as funiculi) as well as the anterior spinal commissure 3,5.Īnterior columns primarily contain the spinothalamic tract s which are responsible for pain, temperature, coarse (non-discriminative) touch and pressure sensationsĭorsal columns contain ascending fibers which are responsible for vibration, conscious proprioception, and fine (discriminative) touch sensations Receive primary afferents from the dorsal roots of the spinal nervesĭivided into ventral and dorsal grey matter commissures Send efferent fibers via the ventral nerve rootsĬontain autonomic neurons for pelvic and visceral organs It is divided into anterior, dorsal and lateral horns and periependymal grey matter 3,5:Ĭontain motor neurons for skeletal muscle The grey matter contains the cell bodies of neurons and glia and is enlarged in the cervical and lumbosacral regions to provide fibers to the large nerve plexuses. There are 31 nerve roots in total:Ī transverse section of the spinal cord shows a peripheral mass of white matter surrounding an ‘H’ or butterfly-shaped central mass of grey matter with a small ependyma-lined central canal filled with CSF 2. The cord is incompletely divided into left and right halves by the posterior median sulcus (shallow) and the anterior median fissure (deep) 6. The spinal cord is segmented by the nerve roots that emerge from it. The spinal cord is divided into cervical, thoracic and lumbar parts and terminates at the conus medullaris at approximately the L1 vertebral body level in adults. Throughout its length paired dorsal and ventral nerve roots enter its dorsolateral and ventrolateral surface respectively. Like the brain, it is composed of grey and white matter, however, opposite to the brain, the grey matter is on the internal aspect of the cord and the white matter tracts are external. The spinal cord measures approximately 42-45 cm in length, ~1 cm in diameter and 35 g in weight.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
